WHAT IS IP ADDRESS ?
Hello
friends my name is Vasu Birla and today we will discuss about the IP address so
let’s start.
Ip
address is a address through which we can identify a particular system within
the network.
IT
is a unique identifier. And those systems who follows TCP/IP protocol uses this
IP address.
IP
structure
IP
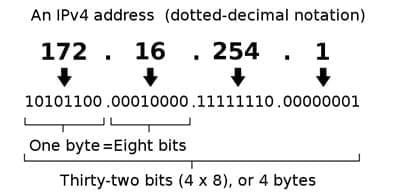
address is also known as Logical address. IT is made of 32 bit for example.
11001000 00001010
00010100 00011110
But
generally we see ip address on systems like 172.16.254.1 because it hard to
remember that is why these 32 bit kept in grouping and these 32 bits will be divided in 4 parts and
it is in decimal system. We use also dotes between these 4 parts of 32
bits. These four section also known as
Octets.
There
is also another address known as Physical address also known as MAC address (
Media access control). This address is
in built on NIC card (Network Interface Card) where we plug the RJ-45 Cable or
Ethernet cable. This physical address is also provide unique identification of
system within network but it has a limitation that this address works on Layer
2 data link layer but when you want to
get connect two different network in that case only layer 3 devices are used
when we need layer 3 address means IP address.
Types
of IP address - there are four
methods for dividing types of ip
addresses.
- Assignment
- Classes
- Public and Private IPs
- Versions
1.
1. Assignment
- there are two types of ip
address in this method –
a. Static
IP address - In this IP address all we
do all configuration manually. Basically in small network or on particular
server we can assign ip address manually
and it doesn’t change itself it is fixed
ip address until we change again manually.
b. Dynamic
IP address – Dynamic IP address means IP
addressed are assigned automatically through DHCP server or APIPA we will discuss about it later.

2.
2. Classes – There are 2 classes of IP address Classful and ClassLess
a.
Classful - In classful 5 Classes of IP
address A,B,C,D and E.
i.
Class A reserved for governments Org or very big
organization. ii. Class B reserved for medium companies.
iii. Class C reserved for small companies.
iv. Class D reserved for Multicasting purpose.
v. Class E reserved for future uses or for experimental purpose.
Here
is some example of Classful classes A,B
and C
Class
A- 35.0.0.0 - Network id – 8 bit
Host address- 24 bit - Begins -
1 to 126
Class
B – 128.5.0.0- network id – 16 bit
- Host address – 16 bit Begins – 128-191
We
can identify class of IP address by its first number when network is not sub-netted or only in
Classful ip address
CLASS A IP address - Lets
have some deep look in class A ip address .
As
we know IP address is made of 32 bits ,
and in this 32 bits first bit of IP add will be always Zero 0 remaining
31 bits will be anything but first bit
of Class A IP address will be 0 always.
Class
A IP address has only 8 bit network part it means we have only 7 bits to make
network part because first bit it 0 – so
by 7 bits we can have only 128 possible address and remaining 24 bits
are for hosts.
In the class A 16 million hosts are available per A class
network. 16 million 777 thousand 216.
But it is impossible to configure 16 m hosts within a single network .
Example of Class A IP address
0nnnnnnn.hhhhhhhh.hhhhhhhh.hhhhhhhh
00000000.00000000.00000000.00000000
To
01111111.11111111.11111111.11111111
First bit of class A begins with 0 always then 7 bits is for
network id and rest 24 bits for hosts
bits.
Range of ip address is
0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 but 0
and 127 is reserved already for special purposes .
0.0.0.0
And
0.255.255.255
These Ip addresses are exceptions in Class A IP address
. all 0s range means 0.0.0.0 represents
default network or my network we can not
assign this ip add to any host.
And 127.0.0.0 range
is also known as loopback address it is used to self testing of network and it
helps to troubleshoot NIC (Network Interface card) using ping commend.
 |
| FIRST FIXED BITS FROM EACH CLASS OF IP |
So these IPs can not be considered in Class A so originally
range of class A is 1 to
126.
Class B IP address
Class B IP address is also consist of 32 bits first 16 bits of network portion and rest 16
bits are for hosts.
Class B IP address begins with 1 and 0
first two bits always will be 1 and 0
So here we have only 14 bits for network portion because
first two bits 1 and 0 is fixed so we have
16384 possible number of networks in Class B.
Remaining 16 bits of hosts
provide us 65536 possible hosts or users.
Example of B class IP add
10nnnnnn.nnnnnnnn.hhhhhhhh.hhhhhhhh
10000000.00000000.00000000.00000000
To
10111111.11111111.11111111.11111111
Except it there is
some exceptions in class B IP adds
its 169.254.x.x we don’t assign this IP address to any
host because this range is already
reserved for APIPA (Automatic Private IP addressing) this IP adds will be automatically configured
by System if there is no DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) service
available for user.
Class C IP address
Class C IP address consists of 32 bits in this first 24 bits are for network portion
and remaining 8 bits are for hosts portion.
Class C IP add are very popular and commonly used by many
service providers and by private networks.
In class C ip address first 3 bits begins with 1,1 and 0
and these bits are fixed.
First 3 bits are 110
these are fixed bits and remaining 21 more bits in network part provide
us over 2 million possible class network
And 8 bits of host part provide us only 256 class c host ip
addresses.
110nnnnn.nnnnnnnn.nnnnnnnn.hhhhhhhh
11000000.00000000.00000000.00000000
To
11011111.11111111.11111111.11111111
It start with 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255
Class D IP address
Class D IP addresses are used for multicasting purposes and its range is 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
These IP adds are used for one to many communication. Multicasting
is a way through which we can get communicate one to many users.
IT is consist of 32 bits and
first 4 bits are always fixed
these 4 bits are 1110.
IT send message to group of hosts we can not communicate one to one means unicasting and one to all means
broadcasting.
Example of multicasting like
video conference , live streaming videos only selected group of
receivers available.
11100000.00000000.00000000.00000000
To
11101111.11111111.11111111.11111111
224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
Some popular Class D IP address used by some special
protocols in routers for example –
224.0.0.5 this class
D IP is used by OSPF protocol to send hello packets.
224.0.0.6 is also used by OSPF router to send routing
information to designated router on a
network segment.
224.0.0.9 this class
D IP add is used by Routing information
Protocol version 2 (RIPv2) to send routing information to all RIPv2 aware
routers on a network segment.
224.0.0.10 this class D IP add is used by EIGRP routing
protocol to send routing info.
224.0.0.18 is used by Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP).
Class E IP address
Class E IPs starts with 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 . These
IP adds are used for experimental purposes but there is no description of these
experimental purposes but some government and bit private organization uses
these IP add.
Consist of 32 bits and first 4 bits are fixed these bits are
1111 lets have look of binary form of This IP
11110000.00000000.00000000.00000000
To
11111111.11111111.11111111.11111111
Means in decimal form
its 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Thanks for reading please share this blog to your friends and subscribe in the next part we will discuss about the third method or types or IP address Public and Private Ip adress .... ok friends.. good luck for life..... Hare krishna...






Comments
Post a Comment